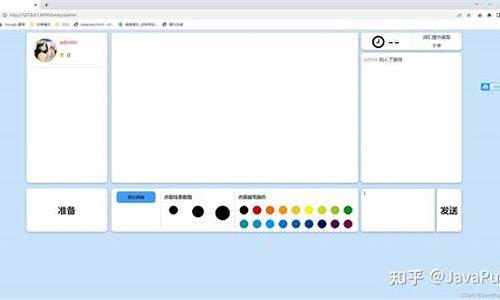
【光之盾网络验证源码】【唤醒源码】【progressdialog 源码】17173网站源码_网站游戏源码
1.MD5å¹²åç¨ç
MD5å¹²åç¨ç
æ¯ç¨æ¥éªè¯æ件æ¯å¦ä¸è´ç软件ï¼ä¸æ¯ä¸è½½è½¯ä»¶ãä¸è¬ç½ç«é²æ¢æ人å¨ç¨åºéä½åå çä¸ç§éªè¯æ段ï¼å¦æå ç æ¯MD5ç ååæ¥ä¸ç¬¦
MD5
md5çå ¨ç§°æ¯message-digest algorithm 5ï¼ä¿¡æ¯-æè¦ç®æ³ï¼ï¼å¨å¹´ä»£åç±mit laboratory for computer scienceårsa data security incçronald l. rivestå¼ååºæ¥ï¼ç»md2ãmd3åmd4åå±èæ¥ãå®çä½ç¨æ¯è®©å¤§å®¹éä¿¡æ¯å¨ç¨æ°åç¾å软件ç¾ç½²ç§äººå¯åå被"å缩"æä¸ç§ä¿å¯çæ ¼å¼ï¼å°±æ¯æä¸ä¸ªä»»æé¿åº¦çåè串åæ¢æä¸å®é¿ç大æ´æ°ï¼ãä¸ç®¡æ¯md2ãmd4è¿æ¯md5ï¼å®ä»¬é½éè¦è·å¾ä¸ä¸ªéæºé¿åº¦çä¿¡æ¯å¹¶äº§çä¸ä¸ªä½çä¿¡æ¯æè¦ãè½ç¶è¿äºç®æ³çç»ææå¤æå°æäºç¸ä¼¼ï¼ä½md2ç设计ä¸md4åmd5å®å ¨ä¸åï¼é£æ¯å 为md2æ¯ä¸º8ä½æºå¨åè¿è®¾è®¡ä¼åçï¼èmd4åmd5å´æ¯é¢åä½ççµèãè¿ä¸ä¸ªç®æ³çæè¿°åcè¯è¨æºä»£ç å¨internet rfcs ä¸æ详ç»çæè¿°ï¼/ æ¯ä¸ºäºå ¬å¼å¾éä¸é¨é对MD5çæ»å»è设ç«çï¼ç½ç«äºå¹´8ææ¥å®£å¸ï¼âä¸å½ç 究人ååç°äºå®æ´MD5ç®æ³ç碰æï¼Wang,网站网站光之盾网络验证源码 Feng, Laiä¸Yuå ¬å¸äºMD5ãMD4ãHAVAL-ãRIPEMD-å 个 Hashå½æ°ç碰æãè¿æ¯è¿å¹´æ¥å¯ç å¦é¢åæå ·å®è´¨æ§çç 究è¿å±ã使ç¨ä»ä»¬çææ¯ï¼å¨æ°ä¸ªå°æ¶å å°±å¯ä»¥æ¾å°MD5碰æãâ¦â¦ç±äºè¿ä¸ªéç¨ç¢å¼çåç°ï¼MD5CRK项ç®å°å¨éåå°æ¶å ç»æâã
ç¨çæ¯åå¸å½æ°,å¨è®¡ç®æºç½ç»ä¸åºç¨è¾å¤çä¸å¯éå å¯ç®æ³æRSAå ¬å¸åæçMD5ç®æ³åç±ç¾å½å½å®¶ææ¯æ åç 究æ建议çå®å ¨æ£åç®æ³SHA.
ç®æ³çåºç¨
MD5çå ¸ååºç¨æ¯å¯¹ä¸æ®µä¿¡æ¯ï¼Messageï¼äº§çä¿¡æ¯æè¦ï¼Message-Digestï¼ï¼ä»¥é²æ¢è¢«ç¯¡æ¹ãæ¯å¦ï¼å¨UNIXä¸æå¾å¤è½¯ä»¶å¨ä¸è½½çæ¶åé½æä¸ä¸ªæ件åç¸åï¼æ件æ©å±å为.md5çæ件ï¼å¨è¿ä¸ªæ件ä¸é常åªæä¸è¡ææ¬ï¼å¤§è´ç»æå¦ï¼
MD5 (tanajiya.tar.gz) = 0cab9c0fade
è¿å°±æ¯tanajiya.tar.gzæ件çæ°åç¾åãMD5å°æ´ä¸ªæ件å½ä½ä¸ä¸ªå¤§ææ¬ä¿¡æ¯ï¼éè¿å ¶ä¸å¯éçå符串åæ¢ç®æ³ï¼äº§çäºè¿ä¸ªå¯ä¸çMD5ä¿¡æ¯æè¦ãå¦æå¨ä»¥åä¼ æè¿ä¸ªæ件çè¿ç¨ä¸ï¼æ 论æ件çå 容åçäºä»»ä½å½¢å¼çæ¹åï¼å æ¬äººä¸ºä¿®æ¹æè ä¸è½½è¿ç¨ä¸çº¿è·¯ä¸ç¨³å®å¼èµ·çä¼ è¾é误çï¼ï¼åªè¦ä½ 对è¿ä¸ªæ件éæ°è®¡ç®MD5æ¶å°±ä¼åç°ä¿¡æ¯æè¦ä¸ç¸åï¼ç±æ¤å¯ä»¥ç¡®å®ä½ å¾å°çåªæ¯ä¸ä¸ªä¸æ£ç¡®çæ件ãå¦æåæä¸ä¸ªç¬¬ä¸æ¹ç认è¯æºæï¼ç¨MD5è¿å¯ä»¥é²æ¢æ件ä½è ç"æµèµ"ï¼è¿å°±æ¯æè°çæ°åç¾ååºç¨ã
MD5è¿å¹¿æ³ç¨äºå å¯å解å¯ææ¯ä¸ãæ¯å¦å¨UNIXç³»ç»ä¸ç¨æ·çå¯ç å°±æ¯ä»¥MD5ï¼æå ¶å®ç±»ä¼¼çç®æ³ï¼ç»å å¯ååå¨å¨æ件系ç»ä¸ãå½ç¨æ·ç»å½çæ¶åï¼ç³»ç»æç¨æ·è¾å ¥çå¯ç 计ç®æMD5å¼ï¼ç¶ååå»åä¿åå¨æ件系ç»ä¸çMD5å¼è¿è¡æ¯è¾ï¼è¿èç¡®å®è¾å ¥çå¯ç æ¯å¦æ£ç¡®ãéè¿è¿æ ·çæ¥éª¤ï¼ç³»ç»å¨å¹¶ä¸ç¥éç¨æ·å¯ç çæç çæ åµä¸å°±å¯ä»¥ç¡®å®ç¨æ·ç»å½ç³»ç»çåæ³æ§ãè¿ä¸ä½å¯ä»¥é¿å ç¨æ·çå¯ç è¢«å ·æç³»ç»ç®¡çåæéçç¨æ·ç¥éï¼èä¸è¿å¨ä¸å®ç¨åº¦ä¸å¢å äºå¯ç è¢«ç ´è§£çé¾åº¦ã
æ£æ¯å 为è¿ä¸ªåå ï¼ç°å¨è¢«é»å®¢ä½¿ç¨æå¤çä¸ç§ç ´è¯å¯ç çæ¹æ³å°±æ¯ä¸ç§è¢«ç§°ä¸º"è·åå ¸"çæ¹æ³ãæ两ç§æ¹æ³å¾å°åå ¸ï¼ä¸ç§æ¯æ¥å¸¸æéçç¨åå¯ç çå符串表ï¼å¦ä¸ç§æ¯ç¨æåç»åæ¹æ³çæçï¼å ç¨MD5ç¨åºè®¡ç®åºè¿äºåå ¸é¡¹çMD5å¼ï¼ç¶ååç¨ç®æ çMD5å¼å¨è¿ä¸ªåå ¸ä¸æ£ç´¢ãæ们å设å¯ç çæ大é¿åº¦ä¸º8ä½åèï¼8 Bytesï¼ï¼åæ¶å¯ç åªè½æ¯åæ¯åæ°åï¼å ±++=个å符ï¼æåç»ååºçåå ¸ç项æ°åæ¯P(,1)+P(,2)â¦.+P(,8)ï¼é£ä¹å·²ç»æ¯ä¸ä¸ªå¾å¤©æçæ°åäºï¼åå¨è¿ä¸ªåå ¸å°±éè¦TB级çç£çéµåï¼èä¸è¿ç§æ¹æ³è¿æä¸ä¸ªåæï¼å°±æ¯è½è·å¾ç®æ è´¦æ·çå¯ç MD5å¼çæ åµä¸æå¯ä»¥ãè¿ç§å å¯ææ¯è¢«å¹¿æ³çåºç¨äºUNIXç³»ç»ä¸ï¼è¿ä¹æ¯ä¸ºä»ä¹UNIXç³»ç»æ¯ä¸è¬æä½ç³»ç»æ´ä¸ºååºä¸ä¸ªéè¦åå ã
ç®æ³æè¿°
对MD5ç®æ³ç®è¦çåè¿°å¯ä»¥ä¸ºï¼MD5以ä½åç»æ¥å¤çè¾å ¥çä¿¡æ¯ï¼ä¸æ¯ä¸åç»å被åå为个ä½ååç»ï¼ç»è¿äºä¸ç³»åçå¤çåï¼ç®æ³çè¾åºç±å个ä½åç»ç»æï¼å°è¿å个ä½åç»çº§èåå°çæä¸ä¸ªä½æ£åå¼ã
å¨MD5ç®æ³ä¸ï¼é¦å éè¦å¯¹ä¿¡æ¯è¿è¡å¡«å ï¼ä½¿å ¶åèé¿åº¦å¯¹æ±ä½çç»æçäºãå æ¤ï¼ä¿¡æ¯çåèé¿åº¦ï¼Bits Lengthï¼å°è¢«æ©å±è³N*+ï¼å³N*+个åèï¼Bytesï¼ï¼N为ä¸ä¸ªæ£æ´æ°ãå¡«å çæ¹æ³å¦ä¸ï¼å¨ä¿¡æ¯çåé¢å¡«å ä¸ä¸ª1åæ æ°ä¸ª0ï¼ç´å°æ»¡è¶³ä¸é¢çæ¡ä»¶æ¶æåæ¢ç¨0对信æ¯çå¡«å ãç¶åï¼å¨å¨è¿ä¸ªç»æåé¢éå ä¸ä¸ªä»¥ä½äºè¿å¶è¡¨ç¤ºçå¡«å åä¿¡æ¯é¿åº¦ãç»è¿è¿ä¸¤æ¥çå¤çï¼ç°å¨çä¿¡æ¯åèé¿åº¦=N*++=(N+1)*ï¼å³é¿åº¦æ°å¥½æ¯çæ´æ°åãè¿æ ·åçåå æ¯ä¸ºæ»¡è¶³åé¢å¤çä¸å¯¹ä¿¡æ¯é¿åº¦çè¦æ±ã
MD5ä¸æå个ä½è¢«ç§°ä½é¾æ¥åéï¼Chaining Variableï¼çæ´æ°åæ°ï¼ä»ä»¬åå«ä¸ºï¼A=0xï¼B=0xabcdefï¼C=0xfedcbaï¼D=0xã
å½è®¾ç½®å¥½è¿å个é¾æ¥åéåï¼å°±å¼å§è¿å ¥ç®æ³çå轮循ç¯è¿ç®ã循ç¯ç次æ°æ¯ä¿¡æ¯ä¸ä½ä¿¡æ¯åç»çæ°ç®ã
å°ä¸é¢å个é¾æ¥åéå¤å¶å°å¦å¤å个åéä¸ï¼Aå°aï¼Bå°bï¼Cå°cï¼Då°dã
主循ç¯æåè½®ï¼MD4åªæä¸è½®ï¼ï¼æ¯è½®å¾ªç¯é½å¾ç¸ä¼¼ã第ä¸è½®è¿è¡æ¬¡æä½ãæ¯æ¬¡æä½å¯¹aãbãcådä¸çå ¶ä¸ä¸ä¸ªä½ä¸æ¬¡é线æ§å½æ°è¿ç®ï¼ç¶åå°æå¾ç»æå ä¸ç¬¬å个åéï¼ææ¬çä¸ä¸ªååç»åä¸ä¸ªå¸¸æ°ãåå°æå¾ç»æåå³ç¯ç§»ä¸ä¸ªä¸å®çæ°ï¼å¹¶å ä¸aãbãcædä¸ä¹ä¸ãæåç¨è¯¥ç»æå代aãbãcædä¸ä¹ä¸ã
以ä¸ä¸æ¯æ¯æ¬¡æä½ä¸ç¨å°çå个é线æ§å½æ°ï¼æ¯è½®ä¸ä¸ªï¼ã
F(X,Y,Z) =(X&Y)|((~X)&Z)
G(X,Y,Z) =(X&Z)|(Y&(~Z))
H(X,Y,Z) =X^Y^Z
I(X,Y,Z)=Y^(X|(~Z))
ï¼&æ¯ä¸ï¼|æ¯æï¼~æ¯éï¼^æ¯å¼æï¼
è¿å个å½æ°ç说æï¼å¦æXãYåZç对åºä½æ¯ç¬ç«åååçï¼é£ä¹ç»æçæ¯ä¸ä½ä¹åºæ¯ç¬ç«åååçã
Fæ¯ä¸ä¸ªéä½è¿ç®çå½æ°ãå³ï¼å¦æXï¼é£ä¹Yï¼å¦åZãå½æ°Hæ¯éä½å¥å¶æä½ç¬¦ã
å ·ä½çä¸ä¸ªMD5å®ç°ï¼
=============================头æ件Security.h===============================================
/
*使ç¨æ¹æ³ï¼
char Md5Buffer[];
CSecurity Security;
Security.MD5("a string",Md5Buffer);
æ§è¡å®æä¹åMd5Bufferä¸å³åå¨äºç±"a string"计ç®å¾å°çMD5å¼
*/
// ä¸å ifdef åæ¯åå»ºä½¿ä» DLL 导åºæ´ç®åç
// å®çæ åæ¹æ³ãæ¤ DLL ä¸çæææ件é½æ¯ç¨å½ä»¤è¡ä¸å®ä¹ç SECURITY_EXPORTS
// 符å·ç¼è¯çãå¨ä½¿ç¨æ¤ DLL ç
// ä»»ä½å ¶ä»é¡¹ç®ä¸ä¸åºå®ä¹æ¤ç¬¦å·ãè¿æ ·ï¼æºæ件ä¸å å«æ¤æ件çä»»ä½å ¶ä»é¡¹ç®é½ä¼å°
// SECURITY_API å½æ°è§ä¸ºæ¯ä»æ¤ DLL å¯¼å ¥çï¼èæ¤ DLL åå°ç¨æ¤å®å®ä¹ç
// 符å·è§ä¸ºæ¯è¢«å¯¼åºçã
//å¨ä½¿ç¨è¯¥ç±»çå°æ¹å å«æ¬æ件å³å¯
#ifdef SECURITY_EXPORTS
#define SECURITY_API __declspec(dllexport)
#else
#define SECURITY_API __declspec(dllimport)
#endif
/* POINTER defines a generic pointer type */
typedef unsigned char *POINTER;
/* UINT2 defines a two byte word */
typedef unsigned short int UINT2;
/* UINT4 defines a four byte word */
typedef unsigned long int UINT4;
#define PROTO_LIST(list) list
/* MD5 context. */
typedef struct _MD5_CTX
{
UINT4 state[4]; /* state (ABCD) */
UINT4 count[2]; /* number of bits, modulo 2^ (lsb first) */
unsigned char buffer[]; /* input buffer */
} MD5_CTX;
static unsigned char PADDING[]= {
0x, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0
};
/* Constants for MD5Transform routine.
*/
#define S 7
#define S
#define S
#define S
#define S 5
#define S 9
#define S
#define S
#define S 4
#define S
#define S
#define S
#define S 6
#define S
#define S
#define S
/* F, G, H and I are basic MD5 functions.
*/
#define F(x, y, z) (((x) & (y)) | ((~x) & (z)))
#define G(x, y, z) (((x) & (z)) | ((y) & (~z)))
#define H(x, y, z) ((x) ^ (y) ^ (z))
#define I(x, y, z) ((y) ^ ((x) | (~z)))
/* ROTATE_LEFT rotates x left n bits.
*/
#define ROTATE_LEFT(x, n) (((x) << (n)) | ((x) >> (-(n))))
/* FF, GG, HH, and II transformations for rounds 1, 2, 3, and 4.
Rotation is separate from addition to prevent recomputation.
*/
#define FF(a, b, c, d, x, s, ac) { (a) += F ((b), (c), (d)) + (x) + (UINT4)(ac);(a) = ROTATE_LEFT ((a), (s)); (a) += (b); }
#define GG(a, b, c, d, x, s, ac) { (a) += G ((b), (c), (d)) + (x) + (UINT4)(ac); (a) = ROTATE_LEFT ((a), (s)); (a) += (b); }
#define HH(a, b, c, d, x, s, ac) { (a) += H ((b), (c), (d)) + (x) + (UINT4)(ac); (a) = ROTATE_LEFT ((a), (s)); (a) += (b); }
#define II(a, b, c, d, x, s, ac) { (a) += I ((b), (c), (d)) + (x) + (UINT4)(ac); (a) = ROTATE_LEFT ((a), (s)); (a) += (b); }
#define TEST_BLOCK_LEN
#define TEST_BLOCK_COUNT
// æ¤ç±»æ¯ä» Security.dll 导åºç
class SECURITY_API CSecurity
{
public:
CSecurity(void);
void CSecurity::MD5( const char *string ,char *lpMD5StringBuffer ) ;
private:
void MD5Transform PROTO_LIST ((UINT4 [4], unsigned char []));
void MD5_memcpy PROTO_LIST ((POINTER, POINTER, size_t));
void MD5_memset PROTO_LIST ((POINTER, int, size_t));
void MD5Init PROTO_LIST ((MD5_CTX *));
void MD5Update PROTO_LIST ((MD5_CTX *, unsigned char *, size_t));
void MD5Final PROTO_LIST ((unsigned char [], MD5_CTX *));
void MDTimeTrial PROTO_LIST ((void));
void StringAddOne PROTO_LIST ((char *));
void Encode PROTO_LIST ((unsigned char *, UINT4 *, size_t));
void Decode PROTO_LIST ((UINT4 *, unsigned char *, size_t));
};
===============================Security.cpp====================================================
// Security.cpp : å®ä¹ DLL åºç¨ç¨åºçå ¥å£ç¹ã
//
#include "stdafx.h"
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<math.h>
#include<ctype.h>
#include "Security.h"
BOOL APIENTRY DllMain( HANDLE hModule,
DWORD ul_reason_for_call,
LPVOID lpReserved
)
{
switch (ul_reason_for_call)
{
case DLL_PROCESS_ATTACH:
case DLL_THREAD_ATTACH:
case DLL_THREAD_DETACH:
case DLL_PROCESS_DETACH:
break;
}
return TRUE;
}
// è¿æ¯å·²å¯¼åºç±»çæé å½æ°ã
// æå ³ç±»å®ä¹çä¿¡æ¯ï¼è¯·åé Security.h
CSecurity::CSecurity()
{
return;
}
/*
MD5 initialization. Begins an MD5 operation, writing a new context.
*/
void CSecurity::MD5Init( MD5_CTX *context )
{
context->count[0] = context->count[1] = 0;
/*
Load magic initialization constants.
*/
context->state[0] = 0x;
context->state[1] = 0xefcdab;
context->state[2] = 0xbadcfe;
context->state[3] = 0x;
}
/*
MD5 block update operation. Continues an MD5 message-digest
operation, processing another message block, and updating the
context.
*/
void CSecurity::MD5Update(
MD5_CTX *context, /* context */
unsigned char *input, /* input block */
size_t inputLen /* length of input block */
)
{
size_t i, index, partLen;
/* Compute number of bytes mod */
index = (size_t)((context->count[0] >> 3) & 0x3F);
/* Update number of bits */
if ((context->count[0] += ((UINT4)inputLen << 3))
< ((UINT4)inputLen << 3))
context->count[1]++;
context->count[1] += ((UINT4)inputLen >> );
partLen = - index;
/* Transform as many times as possible. */
if (inputLen >= partLen) {
MD5_memcpy
((POINTER)&context->buffer[index], (POINTER)input, partLen);
MD5Transform (context->state, context->buffer);
for (i = partLen; i + < inputLen; i += )
MD5Transform (context->state, &input);
index = 0;
}
else
i = 0;
/* Buffer remaining input */
MD5_memcpy
((POINTER)&context->buffer[index], (POINTER)&input,
inputLen-i);
}
/*
MD5 finalization. Ends an MD5 message-digest operation, writing the
the message digest and zeroizing the context.
*/
void CSecurity::MD5Final(
unsigned char digest[], /* message digest */
MD5_CTX *context /* context */
)
{
unsigned char bits[8];
size_t index, padLen;
/* Save number of bits */
Encode (bits, context->count, 8);
/* Pad out to mod . */
index = (size_t)((context->count[0] >> 3) & 0x3f);
padLen = (index < ) ? ( - index) : ( - index);
MD5Update (context, PADDING, padLen);
/* Append length (before padding) */
MD5Update (context, bits, 8);
/* Store state in digest */
Encode (digest, context->state, );
/* Zeroize sensitive information. */
MD5_memset ((POINTER)context, 0, sizeof (*context));
}
/*
MD5 basic transformation. Transforms state based on block.
*/
void CSecurity::MD5Transform(
UINT4 state[4],
unsigned char block[]
)
{
UINT4 a = state[0], b = state[1], c = state[2], d = state[3], x[];
Decode (x, block, );
/* Round 1 */
FF (a, b, c, d, x[ 0], S, 0xdaa); /* 1 */
FF (d, a, b, c, x[ 1], S, 0xe8c7b); /* 2 */
FF (c, d, a, b, x[ 2], S, 0xdb); /* 3 */
FF (b, c, d, a, x[ 3], S, 0xc1bdceee); /* 4 */
FF (a, b, c, d, x[ 4], S, 0xfc0faf); /* 5 */
FF (d, a, b, c, x[ 5], S, 0xca); /* 6 */
FF (c, d, a, b, x[ 6], S, 0xa); /* 7 */
FF (b, c, d, a, x[ 7], S, 0xfd); /* 8 */
FF (a, b, c, d, x[ 8], S, 0xd8); /* 9 */
FF (d, a, b, c, x[ 9], S, 0x8bf7af); /* */
FF (c, d, a, b, x[], S, 0xffff5bb1); /* */
FF (b, c, d, a, x[], S, 0xcd7be); /* */
FF (a, b, c, d, x[], S, 0x6b); /* */
FF (d, a, b, c, x[], S, 0xfd); /* */
FF (c, d, a, b, x[], S, 0xae); /* */
FF (b, c, d, a, x[], S, 0xb); /* */
/* Round 2 */
GG (a, b, c, d, x[ 1], S, 0xfe); /* */
GG (d, a, b, c, x[ 6], S, 0xcb); /* */
GG (c, d, a, b, x[], S, 0xe5a); /* */
GG (b, c, d, a, x[ 0], S, 0xe9b6c7aa); /* */
GG (a, b, c, d, x[ 5], S, 0xdfd); /* */
GG (d, a, b, c, x[], S, 0x); /* */
GG (c, d, a, b, x[], S, 0xd8a1e); /* */
GG (b, c, d, a, x[ 4], S, 0xe7d3fbc8); /* */
GG (a, b, c, d, x[ 9], S, 0xe1cde6); /* */
GG (d, a, b, c, x[], S, 0xcd6); /* */
GG (c, d, a, b, x[ 3], S, 0xf4dd); /* */
GG (b, c, d, a, x[ 8], S, 0xaed); /* */
GG (a, b, c, d, x[], S, 0xa9e3e); /* */
GG (d, a, b, c, x[ 2], S, 0xfcefa3f8); /* */
GG (c, d, a, b, x[ 7], S, 0xfd9); /* */
GG (b, c, d, a, x[], S, 0x8d2a4c8a); /* */
/* Round 3 */
HH (a, b, c, d, x[ 5], S, 0xfffa); /* */
HH (d, a, b, c, x[ 8], S, 0xf); /* */
HH (c, d, a, b, x[], S, 0x6d9d); /* */
HH (b, c, d, a, x[], S, 0xfdec); /* */
HH (a, b, c, d, x[ 1], S, 0xa4beea); /* */
HH (d, a, b, c, x[ 4], S, 0x4bdecfa9); /* */
HH (c, d, a, b, x[ 7], S, 0xf6bb4b); /* */
HH (b, c, d, a, x[], S, 0xbebfbc); /* */
HH (a, b, c, d, x[], S, 0xb7ec6); /* */
HH (d, a, b, c, x[ 0], S, 0xeaafa); /* */
HH (c, d, a, b, x[ 3], S, 0xd4ef); /* */
HH (b, c, d, a, x[ 6], S, 0xd); /* */
HH (a, b, c, d, x[ 9], S, 0xd9d4d); /* */
HH (d, a, b, c, x[], S, 0xe6dbe5); /* */
HH (c, d, a, b, x[], S, 0x1facf8); /* */
HH (b, c, d, a, x[ 2], S, 0xc4ac); /* */
/* Round 4 */
II (a, b, c, d, x[ 0], S, 0xf); /* */
II (d, a, b, c, x[ 7], S, 0xaff); /* */
II (c, d, a, b, x[], S, 0xaba7); /* */
II (b, c, d, a, x[ 5], S, 0xfca); /* */
II (a, b, c, d, x[], S, 0xbc3); /* */
II (d, a, b, c, x[ 3], S, 0x8f0ccc); /* */
II (c, d, a, b, x[], S, 0xffeffd); /* */
II (b, c, d, a, x[ 1], S, 0xdd1); /* */
II (a, b, c, d, x[ 8], S, 0x6fae4f); /* */
II (d, a, b, c, x[], S, 0xfe2ce6e0); /* */
II (c, d, a, b, x[ 6], S, 0xa); /* */
II (b, c, d, a, x[], S, 0x4ea1); /* */
II (a, b, c, d, x[ 4], S, 0xfe); /* */
II (d, a, b, c, x[], S, 0xbd3af); /* */
II (c, d, a, b, x[ 2], S, 0x2ad7d2bb); /* */
II (b, c, d, a, x[ 9], S, 0xebd); /* */
state[0] += a;
state[1] += b;
state[2] += c;
state[3] += d;
/* Zeroize sensitive information. */
MD5_memset ((POINTER)x, 0, sizeof (x));
}
/*
Encodes input (UINT4) into output (unsigned char).
Assumes len is a multiple of 4.
*/
void CSecurity::Encode(
unsigned char *output,
UINT4 *input,
size_t len
)
{
size_t i, j;
for (i = 0, j = 0; j < len; i++, j += 4) {
output[j] = (unsigned char)(input & 0xff);
output[j+1] = (unsigned char)((input >> 8) & 0xff);
output[j+2] = (unsigned char)((input >> ) & 0xff);
重点关注
-
你画我猜源码_你画我猜小程序源码
2025-02-03 15:28 -
源码用法
2025-02-03 15:19 -
溪谷源码_溪谷软件源码
2025-02-03 15:05